Thoracic and lung - جامعة آل البيت · PDF file · 2015-10-13Thoracic...
Transcript of Thoracic and lung - جامعة آل البيت · PDF file · 2015-10-13Thoracic...
06/11/1431
1
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Thoracic and lung
Chapter 7
1
Objectives Respiratory System• Discuss anatomy & Philology of respiratory system
• Specify landmarks of thorax / underlying structures
• State component of health hx
• Describe techniques of inspection, percussion, auscultation and palpation
• Distinguish tones of hyperresonance, resonance, tympany, dullness & flatness
• Compare characteristics of normal breath sounds
• Compare characteristics of abnormal /adventitious breath sounds
• Compare characteristics of sounds produced by vocal fremitus
• Distinguish the assessment findings that are frequently associated with common lung conditions
• Identify causes of abnormal lung sounds
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
2
Structure and FunctionPosition and Surface Landmarks
• Thoracic cage—borders
• Anterior thoracic landmarks
– Suprasternal notch
– Sternum
– Manubriosternal angle
– Costal angle
• Posterior thoracic landmarks
– Vertebra prominens
– Spinous processes
– Inferior border of scapula
– Twelfth rib
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Location finding in the lung• Sternal angel best guide anteriorly • First 7 rips of costal cartilage articulate with
sternum • 8th , 9th ,10th, ribs articulate with costal cartilage just
above them • 11th , and 12th rip are flouting rip • Land mark posteriorly :• 12th rip.• inferior angel of the scapula lies at the level of the
7th ribs.• Spinous process C7 is the most prominent process• Second ICS at the level of Spinous process T1.
4
06/11/1431
5
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Line at the chest
• Mid sternal line
• Mid claviculer line
• Anterior auxiliary line
• Mid auxiliary line
• Posterior auxiliary line
• Scapular line
• Vertebral line
9
Reference Lines (Anterior)
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
6
Reference Lines (Posterior)
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Reference Lines (Lateral)
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
7
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Lung fisher and lobes
• Aneriorly :• Apex of each lung rises about 2-4 cm
above the inner third of the clavicle• The lower border of the lung cross the
6th rib at the midclaviculer line and 8th
rib in the mid auxiliary line Posteriorly• The lower border of the lung lies at
about the level of T10 spinous process
13
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Lung fisher and lobes… continue ..
• Right lung dived into upper , middle and lower lobes
• Left lung dived into uper and lower lobes
• Supracaviculer : above the clavicle• Infraclaviculer: below the clavicle• Interscapular: between the scapula• Infrascapuler; below the scapula 14
06/11/1431
8
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
superior
superior
middle
Inf.
Inf.15
Structures of the Respiratory System
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
9
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
The trachea and major bronchi
• The trachea bifurcates intoo its mainstem bronchie at the level of the sternal angels anteriorly and on the T4 spinous posteriorly
17
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
pleura
• Visceral pleura: serous membrane that cover the outer service of the lung
• Parietal pleura: serous membrane that line the inner rib cage of the upper surface of diaphragm
Function of the pleura: smooth the opposing service and lubricant by plural fluid to allow the ling to move easily with the rib cage
Pleural space: potential space between visceral and parietal pleura.
18
06/11/1431
10
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Breathing
• The dome shaped diaphragm is the primary muscle of inspiration
• Muscle in the rib cage of the neck expand the thoracic during inspiration
• In supine postion : thorax movement slight and abdominal movement easy to see
• Sitting posion; thorax movement becom more promenent
• Accessory muscle : sternomastoed 19
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Inspiration & Expiration
20
06/11/1431
11
Mechanics of Respiration
© Pat Thomas, 2006.
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Changes with age
• The chest wall become stiffer and hardr to move
• Skeltal changes may produce kyphosis this produce barrel chest
22
06/11/1431
12
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Health history • Chest pain• Dyspnya• Wheezing• Cough, sputum• Blood- streaked sputum ( hemoptysis)
• Breathing Patterns– Eupnea: normal, quiet breathing– Apnea: absence of breathing– Labored: increased work of breathing– Paradoxical: chest wall moves in on inspiration &out
on expiration
23
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Technique of Examination of theRespiratory System
Inspection:• Respiratory rate, depth , rythem, ahd effort of
brething• Colore of cyanoses• Supracalviculer retracio• Strider: a chiefly inspiratory wheezes• Shape of the finger nail• Positaion of tha trachia • Shape of the chest :Normal: interior posterior diameter : transverse
diameter = 1:2 24
06/11/1431
13
Normal Adult
25 Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Thoracic Configuration
• Barrel Chest.
• Pectus Carinatum (pigeon chest)• Pectus Excavatum (funnel chest)• Kyphosis• Scoliosis• Kyphoscoliosis• Trauma
26
06/11/1431
14
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Barrel Chest
• increased AP dimeters.
• Normal in children
27
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Pectus Carinatum
• Pectus Carinatum (pigeon chest ) :
The sternum is displaced anteriorly , increase the AP diameter.
28
06/11/1431
15
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Pectus Excavatum
• Pectus Excavatum (funnel chest) : characterized by a depression in the lower portion in the sternum
29
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Kyphosis
• Kyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing of the back, which leads to a hunchback or slouching posture.
30
06/11/1431
16
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Scoliosis
• Scoliosis is a disorder that causes an abnormal curve of the spine
• is a side-to-side curvature of the spine
31
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Kyphoscoliosis
• Abnormal spinal curvature and vertebral rotation deform the chest
32
06/11/1431
17
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Palpation
• palpation of Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues
• Vocal & Tactile Fremitus
• Thoracic Expansion
33
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Skin & Subcutaneous Tissues
• Pain
• Masses
• Subcutaneous Emphysema: air in the subcutaneous space resulting in a crackling sound and sensation when palpated
34
06/11/1431
18
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Vocal & Tactile Fremitus
• Resonance transmitted through chest by speech When assessed, referred to as tactile fremitus
• Patient instructed to repeatedly say, ―ninety-nine.‖
• Fremetuse decrease with : COPD , pleura effusion, fibroses and tumor
• Fremetuse increase : labor pneumonia
• Fremetuse more prominent inner scapular and more prominent left side than right side
35
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Abnormal Tactile Fremitus
Increased
• Pneumonia
• Lung tumor
• Atelectasis
Decreased
• Unilateral– Pneumothorax
– Pleural Effusion
• COPD
• Muscular or obese chest wall
36
06/11/1431
19
Tactile Fremitus - Palpate
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Thoracic Expansion
• Assess for amount and symmetry of chest wall movement
38
06/11/1431
20
Chest Expansion - Palpate
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Percussion
• Assesses resonance of structures inside the thorax• Done by tapping fingers over intercostal spaces• Help to defie whether under luing tissue are air-
filled, fluid-filled or solid • Dullness replaces the resoance when fluid or a solid
tissue replaces air contaning lung • Dullness appear in labor pneumonia(alveoli filed with
flud and blood cells), pleural effusion, fibrous tissue or truma
• Hyper resonance : emphysema, asthma • Diaphragmatic dullness norma 5-6 cm
40
06/11/1431
21
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Percussion Sounds
• Hyperresonance: heard over a hollow structure
• Resonance: heard over air-filled structure
• Dullness: heard over a solid organ
• Flatness: heard over bone
41
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Percussion Technique
42
06/11/1431
22
Sequence to Percussion
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Expected Percussion Findings
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
23
Expected Percussion Findings
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Diaphragmatic Excursion -Percussion
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
24
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Auscultation
• The Stethoscope– Breath Sounds
• Normal Sounds
• Abnormal (Adventitious) Sounds
• Voice sound
47
Sequence for Auscultation
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
25
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Breath Sounds
Normal Sounds (when heard in normal areas)– Tracheal– Bronchial– Vesicular– Bronchovesicular
Breathing sound decreased when air flow is deceased as in obstructive lung disease or muscle weakness
49
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Location where
heard normally
Pitch of
expiratory sound
Intensity of
expiratory sound
Duration of
sound
Over most of
both lung
Relatively lowSoftInspiratory sound
last longer than
expiratory sound
Vesicular
Often in the 1st
and 2nd ICS
anteriolrly and
between scapula
IntermediateIntermediateInspiratory and
expiratory sounds
are about equal
Broncho-
vesiculer
Over the
manubrium
Relatively highLoudExpiratory sound
last longer than
insiratory
Bronchial
Over the trachea Relatively high Very loudInspiratory and
expiratory are
equal
Tracheal
Characteristic of breathing sound
50
06/11/1431
26
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Abnormal (Adventitious) Sounds
• Pleural Friction Rub
• Stridor
• Crackele (rales)
• Ronchi sound ( secretion in large air way).
• Weezes
51
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Bronchial
• Abnormal when heard over lung tissue
• Indicates an underlying density• Pneumonia with consolidation
• Large tumor
• NOT a pleural effusion
52
06/11/1431
27
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Crackles
• Coarse– Low-pitched, sounds like the bubbling of air
through liquid– May be heard on inspiration and/or expiration
(usually expiration)– Caused by: Secretions in the airways or fluid or
secretion in the lung – May clear after suctioning or coughing– Abnormality of the lung as pnemonia, fibroses,
early congestive heart failer and bronchites
53
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Wheezes
• Continuous sound with a musical quality
• May be heard on inspiration and/or expiration (usually expiration only)
• Caused by narrowing of airway lumen (i.e. mucus, edema, bronchospasm or foreign body), heared also in asthma and COPD
54
06/11/1431
28
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Stridor
• High-pitched wheeze-like sound
• May be heard on inspiration and/or expiration (usually inspiration)
• Caused by narrowing of subglottic area (i.e. inflammation, edema or foreign body)
• More dangerous in children & infants due to smaller airway size
55
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
• If any abnormal sound detected should describe loudness, number, and timimg in respiratory cycle
• Clearing crackles, weezese or rhonchi by couph suggested that secretion caused them
56
06/11/1431
29
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Voice Sounds( spoken or whispered sound)
• Egophany
• Bronchophony
• Whispered Pectoriloquy
• Increased transmeted voice sound suggested that air-filled lung has becom air less
• Normal should heared muffled and indistinct
57
Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Bronchophony– Auscultate while patient repeats, ―99, 99 …‖
– Sounds are heard more clearly over consolidation
Ego phony: E heared A
Whispered Pectoriloquy– Auscultate while patient repeated whispers,―1-2-3‖
or ―99-99-99‖
– Sounds are heard more clearly over consolidation
58
06/11/1431
33
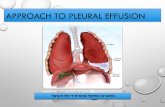
Pleural Effusion
65 Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
66 Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
06/11/1431
35
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
69 Ra'eda AL-mashaqba
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
70 Ra'eda AL-mashaqba