IT Supply Chain Management
-
Upload
preshita-chaurasiya -
Category
Business
-
view
165 -
download
0
description
Transcript of IT Supply Chain Management

Enterprise Business Systems

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 2
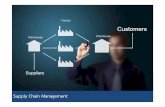
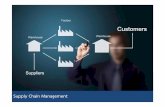
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Fundamentally, supply chain management helps a companyGet the right productsTo the right placeAt the right time In the proper quantityAt an acceptable cost

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 3
Goals of SCM The goal of SCM is to efficiently
Forecast demandControl inventoryEnhance relationships with customers,
suppliers, distributors, and othersReceive feedback on the status of every link
in the supply chain

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 4
What is a Supply Chain? The interrelationships
With suppliers, customers, distributors, and other businesses
Needed to design, build, and sell a product Each supply chain process should add value to
the products or services a company producesFrequently called a value chain

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 5
Supply Chain Life Cycle

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 6
Electronic Data Interchange One of the earliest uses of information
technology for supply chain management The electronic exchange of business transaction
documents between supply chain trading partners
The almost complete automation of an e-commerce supply chain process
Many transactions occur over the Internet, using secure virtual private networks

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 7
Typical EDI Activities

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 8
Roles and Activities of SCM in Business

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 9
Planning & Execution Functions of SCM Planning
Supply chain designCollaborative demand and supply planning
ExecutionMaterials managementCollaborative manufacturingCollaborative fulfillmentSupply chain event managementSupply chain performance management

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 10
Benefits and Challenges of SCM Key Benefits
Faster, more accurate order processingReductions in inventory levelsQuicker times to marketLower transaction and materials costsStrategic relationships with supplier

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 11
Goals and Objectives of SCM

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 12
Benefits and Challenges of SCM Key Challenges
Lack of demand planning knowledge, tools, and guidelines
Inaccurate data provided by other information systems
Lack of collaboration among marketing, production, and inventory management
SCM tools are immature, incomplete, and hard to implement

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 13
Trends in SCM

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 14
ERP: The Business Backbone ERP is a cross-functional enterprise backbone
that integrates and automates processes withinManufacturingLogisticsDistributionAccountingFinanceHuman resources

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 15
What is ERP? Enterprise resource planning is a cross-
functional enterprise system An integrated suite of software modulesSupports basic internal business processesFacilitates business, supplier, and customer
information flows

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 16
ERP Application Components

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 17
ERP Process and Information Flows

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 18
Benefits and Challenges of ERP
ERP Business BenefitsQuality and efficiencyDecreased costsDecision supportEnterprise agility
ERP CostsRisks and costs are considerableHardware and software are a small part
of total costsFailure can cripple or kill a business

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 19
Costs of Implementing a New ERP

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 20
Causes of ERP Failures Most common causes of ERP failure
Under-estimating the complexity of planning, development, training
Failure to involve affected employees in planning and development
Trying to do too much too fast Insufficient training Insufficient data conversion and testingOver-reliance on ERP vendor or consultants

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 21
Trends in ERP

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 22
Customer Relationship Management A customer-centric focus
Customer relationships have become a company’s most valued asset
Every company’s strategy should be to find and retain the most profitable customers possible

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 23
What is CRM? Managing the full range of the customer
relationship involvesProviding customer-facing employees with a
single, complete view of every customer at every touch point and across all channels
Providing the customer with a single, complete view of the company and its extended channels
CRM uses IT to create a cross-functional enterprise system that integrates and automates many of the customer-serving processes

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 24
Application Clusters in CRM

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 25
Contact and Account Management CRM helps sales, marketing, and service
professionals capture and track relevant data aboutEvery past and planned contact with
prospects and customersOther business and life cycle events of
customers Data are captured through customer touchpoints
Telephone, fax, e-mailWebsites, retail stores, kiosksPersonal contact

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 26
Sales A CRM system provides sales reps with the
tools and data resources they need toSupport and manage their sales activitiesOptimize cross- and up-selling
CRM also provides the means to check on a customer’s account status and history before scheduling a sales call

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 27
Marketing and Fulfillment CRM systems help with direct marketing
campaigns by automatic such tasks asQualifying leads for targeted marketingScheduling and tracking mailingsCapturing and managing responsesAnalyzing the business value of the campaignFulfilling responses and requests

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 28
Customer Service and Support A CRM system gives service reps real-time
access to the same database used by sales and marketingRequests for service are created, assigned,
and managedCall center software routes calls to agentsHelp desk software provides service data
and suggestions for solving problems Web-based self-service enables customers to
access personalized support information

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 29
Retention and Loyalty Programs It costs 6 times more to sell to a new customer An unhappy customer will tell 8-10 others Boosting customer retention by 5 percent can boost profits
by 85 percent The odds of selling to an existing customer are 50 percent;
a new one 15 percent About 70 percent of customers will do business with the
company again if a problem is quickly taken care of Enhancing and optimizing customer retention and loyalty
is a primary objective of CRM Identify, reward, and market to the most loyal
and profitable customers Evaluate targeted marketing and relationship programs

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 30
The Three Phases of CRM

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 31
Benefits of CRM Benefits of CRM
Identify and target the best customersReal-time customization and personalization
of products and servicesTrack when and how a customer contacts
the companyProvide a consistent customer experienceProvide superior service and support across
all customer contact points

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 32
CRM Failures Business benefits of CRM are not guaranteed
50 percent of CRM projects did not produce promised results
20 percent damaged customer relationships Reasons for failure
Lack of understanding and preparationNot solving business process problems firstNo participation on part of business
stakeholders involved

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 33
Trends in CRM Operational CRM
Supports customer interaction with greater convenience through a variety of channels
Synchronizes customer interactions consistently across all channels
Makes the company easier to do business with Analytical CRM
Extracts in-depth customer history, preferences, and profitability from databases
Allows prediction of customer value and behavior Allows forecast of demand Helps tailor information and offers to customer needs

Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems 34
Trends in CRM Collaborative CRM
Easy collaboration with customers, suppliers, and partners Improves efficiency and integration throughout supply
chain Greater responsiveness to customer needs through
outside sourcing of products and services
Portal-based CRM Provides users with tools and information that fit their
needs Empowers employees to respond to customer demands
more quickly Helps reps become truly customer-faced Provides instant access to all internal and external
customer information





![[ Aplicativos ] Supply Chain Management](https://static.fdocument.pub/doc/165x107/5571f1bf49795947648b9fa5/-aplicativos-supply-chain-management.jpg)