2-1revisedsyllabus1
Transcript of 2-1revisedsyllabus1
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
1/6
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY KAKINADA
II B.TECH.I SEMESTER (COMMON FOR COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING AND
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY)
REVISED COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS2010-11 BATCH
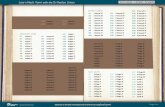
II Year I Semester I SEMESTER P C
S.No. Subject P C
1 Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis 4+1* 4
2 Probability & Statistics 4+1* 4
3 Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science and Engineering 4+1* 4
4 Digital Logic Design 4+1* 4
5 Electronic Devices and Circuits 4+1* 4
6 Data Structures 4+1* 4
7 Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab 3 2
8 Data Structures Lab 3 2
9 Professional Communicational skills 2 1
Total Credits 29
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY KAKINADA
B.TECH. (COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING)II Year B.Tech.I Sem.
DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
Unit I : Number Systems
Binary, Octal, Decimal, Hexadecimal Number Systems. Conversion of Numbers From One Radix To
Another Radix , rs Complement and (r-1)s Complement Subtraction of Unsigned Numbers,
Problems, Signed Binary Numbers, Weighted and Non weighted codes
Unit II:Logic Gates And Boolean Algebra
Basic Gates NOT, AND, OR, Boolean Theorms,Complement And Dual of Logical Expressions,Universal Gates, Ex-Or and Ex-Nor Gates, SOP,POS, Minimizations of Logic Functions Using
Boolean Theorems, Two level Realization of Logic Functions Using Universal Gates. Verilog
programming for the minimized logic functions.Unit III: Gate- Level MinimizationKarnaugh Map Method(K-Map): Minimization of Boolean Functions maximum upto Four Variables, POS And SOP, Simplifications With Dont Care Conditions Using K-Map.
Unit IV: Combinational Arithmetic Logic Circuits
Design of Half Adder, Full Adder, Half Subtractor , Full Subtractor, Ripple Adders and Subtractors,
Ripple Adder/Subtractor Using Ones and Twos Complement Method. Serial Adder , Carry LookAhead Adder.
Unit V: Combinational Logic Circuits
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
2/6
Design of Decoders, Encoders, Multiplexers, Demultiplexers, Higher Order Demultiplexers andMultiplexers, Realization of Boolean Functions Using Decoders and Multiplexers, Priority Encoder,
Code Converters, Magnitude Comparator.
Unit VI: Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices (PLOs)PLA, PAL, PROM. Realization of Switching Functions Using PROM, PAL and PLA. Comparison ofPLA, PAL and PROM..
Unit VII: Introduction to Sequential Logic Circuits
Classification of Sequential Circuits, Basic Sequential Logic Circuits: Latch and Flip-Flop, RS-
Latch Using NAND and NOR Gates, Truth Tables. RS,JK,T and D Flip Flops , Truth and ExcitationTables, Conversion of Flip Flops. Flip Flops With Asynchronous Inputs (Preset and Clear).
Unit VIII: Registers and Counters
Design of Registers, Buffer Register, Control Buffer Registers, Bidirectional Shift Registers,
Universal Shift Register, Design of Ripple Counters, Synchronous Counters and Variable ModulusCounters, Ring Counter, Johnson Counter.
TEXT BOOKS :
1. Digital Design ,4/e, M.Morris Mano, Michael D Ciletti, PEA
2. Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5/e, Roth, CengageREFERENCE BOOKS
1. Switching and Finite Automata Theory,3/e,Kohavi, Jha, Cambridge.2. Digital Logic Design, Leach, Malvino, Saha,TMH
3.Modern Digital Electronics, R.P. Jain, TMH
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY KAKINADA
B.TECH. (COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING)II Year B.Tech.I Sem.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
Unit-I
Electron Ballistics and Applications: Force on Charged Particles in Electric field, Constant Electric
Field, Potential, Relationship between Field Intensity and Potential, Two Dimensional Motion,Electrostatic Deflection in Cathode ray Tube, CRO, Force in Magnetic Field, Motion in MagneticField, Magnetic Deflection in CRT, Magnetic Focusing, Parallel Electric and Magnetic fields andPerpendicular Electric and Magnetic Fields.
Unit- II
Review of Semi Conductor Physics : Insulators, Semi conductors, and Metals classification usingEnergy Band Diagrams, Mobility and Conductivity, Electrons and holes in Intrinsic Semi conductors,Extrinsic Semi Conductor, (P and N Type semiconductor) Hall effect, Generation andRecombination of Charges, Diffusion, Continuity Equation, Injected Minority Carriers, Law of
Junction, Fermi Dirac Function, Fermi level in Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductor
Unit- III
Junction Diode Characteristics : Open circuited P N Junction, Forward and Reverse Bias, Currentcomponents in PN Diode, Diode Equation,Volt-Amper Characteristic, Temperature Dependence on
V I characteristic, Step Graded Junction, Diffusion Capacitance and Diode Resistance (Static and
Dynamic), Energy Band Diagram of PN Diode,
Special Diodes: Avalanche and Zener Break Down, Zener Characterisitics, Tunnel Diode,
Characteristics with the help of Energy Band Diagrams, Varactor Diode, LED, PIN Diode, PhotoDiode
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
3/6
Unit IV
Rectifiers and Filters: Half wave rectifier, ripple factor, full wave rectifier(with and without
transformer), Harmonic components in a rectifier circuit, Inductor filter, Capacitor filter, L- section
filter, - section filter, Multiple L- section and Multiple section filter, and comparison of variousfilter circuits in terms of ripple factors, Simple circuit of a regulator using zener diode, Series andShunt voltage regulators
Unit- V
Transistors :
Junction transistor, Transistor current components, Transistor as an amplifier, Characteristics ofTransistor in Common Base and Common Emitter Configurations, Analytical expressions for
Transistor Characteristics, Punch Through/ Reach Through, Photo Transistor, Typical transistorjunction voltage values.
Unit VI
Field Effect Transistors:
JFET characteristics (Qualitative and Quantitative discussion), Small signal model of JFET,MOSFET characteristics (Enhancement and depletion mode), Symbols of MOSFET, Introduction toSCR and UJT and their characteristics,
UNIT-VIITransistor Biasing and Thermal Stabilization : Transistor Biasing and Thermal Stabilization:Operating point, Basic Stability, Collector to Base Bias, Self Bias Amplifiers, Stabilization againstvariations in VBE,, and for the self bias circuit, Stabilization factors, (S, S', S'), Bias Compensation,
Thermistor and Sensitor compensation, Compensation against variation in VBE, Ico,, Thermalrunaway, Thermal stability
UNIT- VIII
Small signal low frequency Transistor models: Two port devices and the Hybrid model, Transistor
Hybrid model, Determination of h-parameters from characteristics, Measurement of h-parameters,Conversion formulas for the parameters of three transistor configurations, Analysis of a TransistorAmplifier circuit using h- parameters, Comparison of Transistor Amplifier configurations
Text Books:
1. Electronic Devices and CircuitsJ. Millman, C.C. Halkias, Tata Mc-Graw Hill
Reference
1. Electronic Devices and CircuitsK Satya Prasad, VGS Book Links2. Integrated ElectronicsJacob Millman, Chritos C. Halkies,, Tata Mc-Graw Hill, 20093. Electronic Devices and CircuitsSalivahanan, Kumar, Vallavaraj, TATA McGraw Hill, Second
Edition
4. Electronic Devices and CircuitsR.L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky, Pearson/PrenticeHall,9thEdition,20065. Electronic Devices and Circuits -BV Rao, KBR Murty, K Raja Rajeswari, PCR Pantulu, Pearson,
2nd edition
For More Jntuk Stuff Follow us @ strikingsoon.com & Then from the home page select Jntuk
Portal to get Ultimate Stuff Of Jntu World
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
4/6
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY KAKINADA
B.TECH. (COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING)
II Year B.Tech.I Sem.DATA STRUCTURES
UNIT I: Recursion and Linear Search:
Preliminaries of algorithm, Algorithm analysis and complexity.
Recursion: Definition, Design Methodology and Implementation of recursive algorithms, Linear andbinary recursion, recursive algorithms for factorial function, GCD computation, Fibonacci sequence,
Towers of Hanoi, Tail recursionList Searches using Linear Search, Binary Search,Fibonacci Search,
UNIT II: Sorting Techniques:
Basic concepts, Sorting by : insertion (Insertion sort), selection (heap sort), exchange (bubble sort,quick sort), distribution (radix sort ) and merging (merge sort )Algorithms.
UNIT III: Stacks and Queues:
Basic Stack Operations, Representation of a Stack using Arrays, Stack Applications: Reversing list,
Factorial Calculation, In-fix- to postfix Transformation, Evaluating Arithmetic Expressions
Queues: Basic Queues Operations, Representation of a Queue using array, Implementation of QueueOperations using Stack, Applications of Queues-Round robin Algorithm, Enqueue, Dequeue,Circular Queues, Priority Queues.
UNIT IV: Linked Lists:
Introduction, single linked list, representation of a linked list in memory, Operations on a single
linked list, merging two single linked lists into one list, Reversing a single linked list, applications ofsingle linked list to represent polynomial expressions and sparse matrix manipulation, Advantages
and disadvantages of single linked list, Circular linked list, Double linked list
UNIT V: Trees:
Basic tree concepts, Binary Trees: Properties, Representation of Binary Trees using arrays and linked
lists, operations on a Binary tree , Binary Tree Traversals (recursive), Creation of binary tree from in-
order and pre(post)order traversals,
UNIT VI: Advanced concepts of Trees:
Tree Travels using stack (non recursive), Threaded Binary Trees. Binary search tree, Basic concepts,BST operations: insertion, deletion,
Balanced binary treesneed, basics and applications in computer science (No operations )
UNIT VII: Graphs:
Basic concepts, Representations of Graphs: using Linked list and adjacency matrix, Graph algorithmsGraph Traversals (BFS & DFS), applications: Dijkstras shortest path, Transitive closure, Minimum
Spanning Tree using Prims Algorithm, warshalls Algorithm.
Unit VIII: Sets:
Definition, Representation of Sets using Linked list, operations of sets using linked lists, applicationof sets- Information storage using bit stringsAbstract Data Type Introduction to abstraction, Model for an Abstract Data Type, ADT Operations,ADT Data Structure, ADT Implementation of stack and queue .
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Data Structures, 2/e, Richard F, Gilberg , Forouzan, Cengage
2. Data Structures and Algorithms, 2008,G.A.V.Pai, TMH
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
5/6
REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Data Structure with C, Seymour Lipschutz, TMH
2. Classic Data Structures, 2/e, Debasis ,Samanta,PHI,2009
3. Fundamentals of Data Structure in C, 2/e, Horowitz,Sahni, Anderson Freed,University PreesJAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY KAKINADAB.TECH. (COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING)
II Year B.Tech.I Sem.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
PART A : (Only for viva voce Examination)
ELECTRONI C WORKSHOP PRACTICE ( in 6 lab sessions) :
1. Identification, Specifications, Testing of R, L, C Components (Colour Codes), Potentiometers,Switches (SPDT, DPDT, and DIP), Coils, Gang Condensers, Relays, Bread Boards.
2. Identification, Specifications and Testing of Active Devices, Diodes, BJTs, Lowpower JFETs,MOSFETs, Power Transistors, LEDs, LCDs, Optoelectronic Devices, SCR, UJT, DIACs,
TRIACs, Linear and Digital ICs.3. Soldering practiceSimple Circuits using active and passive components.4. Single layer and Multi layer PCBs (Identification and Utility).
5. Study and operation of Multimeters (Analog and Digital)
Function Generator Regulated Power Supplies1. Study and Operation of CRO.
PART B : (For Laboratory examination Minimum of 10 experiments)
1. Frequency measurment using Lissajous Figures
2. PN Junction diode characteristics A. Forward bias B. Reverse bias.( cut-in voltage &Resistance calculations)
3. Zener diode characteristics and Zener as a regulator4. Transistor CB characteristics (Input and Output) & h Parameter calculations5. Transistor CE characteristics (Input and Output) & h Parameter calculations6. Rectifier without filters (Full wave & Half wave)
7. Rectifier with filters (Full wave & Half wave)
8. FET characteristics9. SCR Charecteristics10. UJT Charectristics
11. CE Amplifier12. CC Amplifier (Emitter Follower).
PART C:Equipment required for Laboratories:
1. Regulated Power supplies (RPS) - 0-30v
2. CROs - 0-20M Hz.
3. Function Generators - 0-1 M Hz.
4. Multimeters
5. Decade Resitance Boxes/Rheostats
-
8/22/2019 2-1revisedsyllabus1
6/6
6. Decade Capacitance Boxes
7. Micro Ammeters (Analog or Digital) - 0-20 A, 0-50A, 0-100A, 0- 200A
8. Voltmeters (Analog or Digital) - 0-50V, 0-100V, 0-250V
9. Electronic Components - Resistors, Capacitors, BJTs, LCDs, SCRs, UJTs, FETs, LEDs,
MOSFETs,diodes,transistors