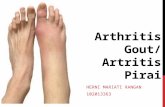
Trends and Insights in Gout (PRA 2015)
-
Upload
philippine-rheumatology-association -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
473 -
download
1
Transcript of Trends and Insights in Gout (PRA 2015)
Several milestones have marked the progress of hyperuricemia and gout. Our aims now are to understand more of the genesis of hyperuricemia, to prevent the development of symptomatic gout, and to avoid its complication
Schumacher, R.
! 40 y.o. male, DM of a pharma company ! sudden onset of pain ! swelling of the right knee ! (+) history going out with MD’s, 2 days prior to
symptoms Past History -‐ joint pains x 4-‐5 yrs -‐ 3 months PTC: Hypertension, Dyslipidemia
▪ Losartan OD ▪ Aspirin OD ▪ Aldazide prn ▪ Statin OD
! Why is Gout of particular importance at present times ?
-‐ increasing frequency -‐ changing clinical spectrum -‐ under diagnosis, under treatment -‐ new mechanisms ( IL-‐1, inflammasomes) -‐ new treatment ( IL-‐1 inhibitors, feboxustat, uricase) -‐ potential usefulness of imaging -‐ new understanding of disease course and comorbidities
! What do we use ? -‐ Treat the inflammation -‐ NSAID’s, Colchicine, Steroids Biologics? -‐ Treat the biochemical hallmark (HU) -‐ urate lowering agents -‐ uricase -‐ Non pharmacologic therapy
! What do we use ? -‐ Treat the inflammation -‐ NSAID’s, Colchicine, Steroids Biologics? -‐ Treat the biochemical hallmark (HU) -‐ urate lowering agents -‐ uricase -‐ Non pharmacologic therapy
! What do we use ? -‐ Treat the inflammation -‐ NSAID’s, Colchicine, Steroids Biologics? -‐ Treat the biochemical hallmark (HU) -‐ urate lowering agents -‐ uricase -‐ Non pharmacologic therapy
CClr > 60 CClr 40-60
CClr 30-40 CClr < 30
0.6 mg BID 0.6 mg QD
0.6 mg Q2 Days 0.6 mg Q3 Days
- COLCHICINE NOT EXTRACTED BY DIALYSIS - DO NOT USE IN DIALYSIS PATIENTS
- REDUCE COLCHICINE BY 50% FOR AGE >/= 70 - CAUTION WITH DRUG INTERACTIONS e.g., CSA, Statins, Macrolides, Gemfibrozil
! No consensus when to start -‐ Experts recommend that pts with recurrent polyarthritis ,(+) tophi be placed on urate lowering drugs -‐ EULAR, BSR, ACR recommendation Goal: < 6 mg/L ACR, EULAR; < 5 mg/L BSR
Crea clearance maintenance dose (ml / min) Allopurinol 0 100 mg every 3 days 10 100 mg every 2 days 20 100 mg daily 40 150 mg daily 60 200 mg daily 80 250 mg daily 100 300 mg daily 120 350 mg daily 140 400 mg daily
Dalbeth N, Arthritis Rheum 2007
Mechanism of action of urate-‐lowering strategies
Uricase
Uricosurics -‐ probenecid -‐Sulphinpyrazone -‐ Benzbromarone
+
Purine-‐poor diet -‐
NSAIDs Colchicine
Corticosteroids
-‐
Uricostatics -‐ Alloprurinol -‐ Febuxostat
-‐
Renal elimination of uric acid
Purine-‐rich diet
Purines High endurance Purine metabolism
e.g. Myeloproliferative
Disease Lymphoproliferative
disease
Hyperinsulinaemia Hypertension
Diuretics Low-‐dose aspirin
Xanthine
Allantoin
Urate
Hyperuricaemia Low temperature
Low pH
Inflammation
Deposition of Urate crystals
+ +
+
+
-‐
Asymptomatic hyperuricaemia
No therapy
1-‐2 gout attacks
Initiate acute Treatment (NSAIDs, Colchicine, or steroids)
Remove prophylactic therapy if appropriate
And keep Patient on urate-‐ Lowering therapy
(6 months)
Check sUA level
(6 months)
Check sUA level
Check sUA level
(>2 weeks)
Consider Initiating long-‐term Urate-‐lowering
therapy and prophylaxis
(colchicine or NSAIDs) With a target sUA
<6mg/dL
Long-‐term follow-‐up of gout
! Lack of understanding of causes and consequences of gout
! Gout not associated as “serious”, associated with “humor”
! Considered as man’s disease, men reluctant and women unwilling or embarrassed to seek treatment
! Considered as part of aging process, self inflicted by overindulgence and poor lifestyle, often viewed as stigma
! Do not adhere to pharmacologic treatment
! Lack of understanding of causes and consequences of gout
! Manage gout only as acute disease ! Do not educate patients to encourage adherence to therapy
! Do not utilize clinical guidelines for gout ! Lack training in best ways to diagnose and treat gout
! Lack incentives to improve treatment of gout
NSAID’s -‐ puts out the fire Colchicine prophylaxis – keeps matches damp Xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosuric agents -‐ removes the matches