Procedures in RFLP
description
Transcript of Procedures in RFLP

Procedures in RFLPProcedures in RFLP



RFLP analysis can detectRFLP analysis can detect
• Point mutations• Length mutations• Inversions

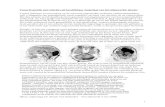
Effect of base changes on RFLP DNA profilesEffect of base changes on RFLP DNA profiles
Reference──GATC───GATC───── A
Base substitution
──GACC───GATC───── B
Deletion─────────────── C
Addition───────────────── D
Inversion────┬──────────── E
a b c
a b c
a c
a b’ b c
h g c
e
d
c── ── ── ── ──
── ── ── ──── ── ── ── ──── ── ── ── ──
── ── ── ── ──
── ── ── ──
── 10── 9
── 8
── 7
── 6
── 5
── 4
── 3
── 2
── 1
── ── ── ── ──
gd
be
a
f
h
-
+
P = DNA marker Restriction site
── ── ── ──
f


Limitations in RFLPLimitations in RFLP
• Intensive work• High cost• High amount of DNA• Use of radioactive

• Co-dominant data (isozymes, RFLPs, SSRs)– Percentage of polymorphic loci, P– Mean no. of alleles per locus, A
– Effective no. of alleles per locus, Ae
• Ae = 1/ i i2 = 1/(1- He)
i is i-th allele frequency
Genetic diversity parametersGenetic diversity parameters

Genetic diversity parametersGenetic diversity parameters
• Co-dominant data (isozymes, RFLPs, SSRs)
– Observed heterozygosity per locus, Ho
– Expected heterozygosity per locus, He
• He = (1- i i2 )
i is i-th allele frequency

Genetic diversity parametersGenetic diversity parameters
• Co-dominant data (isozymes, RFLPs, SSRs)
– Fixation index, Fis
• Fis = 1- Ho/He
– Genetic differentiation, GST
• GST = DST/HT where HT = Hs + DST
HT is total gene diversity; HS is gene diversity within population; DST is gene diversity between population

Genetic diversity parametersGenetic diversity parameters
• Co-dominant data (isozymes, RFLPs, SSRs)– Genetic similarity, I
• Jxy / JxJy
where J = 1- He, X = population X; Y = population Y
– Genetic distance, D• D = -ln I

Genetic diversity parametersGenetic diversity parameters
• VNTR used as probes in RFLP analysis– Percentage of polymorphic loci– Shannon diversity index, H
• H = ni=1 -i ln i
– Genetic similarity, F
• F = 2mxy / (mx+my)
mxy is number of shared fragments by X and Y
mx is number of fragments present in X
my is number fragments present in Y
– Genetic distance, 1- F