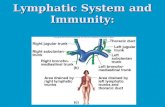
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM - zona.fmed.uniba.sk › fileadmin › lf › sucasti › Teoreticke_ustav… ·...
Transcript of LYMPHATIC SYSTEM - zona.fmed.uniba.sk › fileadmin › lf › sucasti › Teoreticke_ustav… ·...
Unencapsulated lymphoid
tissue
• Lymphoid follicles (nodules)
• Urinary tract
• Digestive tract (Peyer’s patches)
• Upper respiratory tract
SPLEEN
• Vascular and lymphoid tissue
• Left hypochondrium (regio hypochondriaca
sinistra)
• 12 cm long, 7 cm broad (adult)
• 80 – 300 g (adult)
SPLEEN
• Function
– Phagocytosis (removal of particulate material
including aging erythrocytes)
– Pitting of red blood cells
– Immune responses (humoral, cellular)
– cytopoiesis
SPLEEN
• Diaphragmatic surface
– Convex and smooth
• Visceral surface
– Gastric, renal, colic and pancreatic impressions
– Hilum
SPLEEN
• Superior border
– Convex
– Separating diapgragmatic surface from gastric
impression
• Inferior border
– Separating diapgragmatic surface from renal
impression
– Lower margin of 11th rib
SPLEEN
• Posterior extremity
– Faces the vertebral column
• Anterior extremity
– Forms margin connecting the superior and inferior
borders
– Related to the left colic flexure
SPLEEN
• Peritoneum
– Firmly adheres to the splenic capsule
– Peritoneal folds (splenorenal ligament, gastrosplenic
ligament)
• Connective tissue trabeculae
– Fibrous skeleton of spleen
– Supporting delicate tissues of spleen (red pulp, white
pulp)
SPLEEN
• Surface anatomy
– Position assessed by percussion
– Dull area extends over the 9th to 11th ribs
– Should not go forward beyond the midaxillary line
– Normal spleen is not palpable
SPLEEN
• Vessels and nerves
– Splenic artery (branch of the coeliac artery)
– In the splenorenal ligament divids into segmental
branches
– Enter hilum to supply splenic segments
– Each artery ramifies in the trabeculae to supply
parenchyma and capsule
SPLEEN
• Vessels and nerves
– Minor veins pass from red pulp into the trabeculae
– Form segmental veins leaving the hilum to the
splenorenal ligament
– The splenic vein drains directly into the hepatic
portal vein
SPLEEN
• Vessels and nerves
– Lymphatics drain along the trabeculae
– Pass out of the hilum into lymphatic vessels
accompanying the splenic artery and vein
– Splenic lymph goes to pancreatosplenic and coeliac
lymph nodes
– Sympathetic fibers from coeliac plexus (vasomotor)
– Regulates blood flow through the spleen
SPLEEN
• White pulp
– Lymphoid tissue
– B and T lymphocyte maturation an proliferation
– Adventitia of arterioles within trabeculae repalced
by sheath of T lymphocytes (periarteriolar
lymphatic sheath)
– Enlarged lymphoid follicles (Malpighian bodies)
SPLEEN
• White pulp
– Enlarged lymphoid follicles (Malpighian bodies)
– Aggregations of B lymphocytes
– At terminal branches of arterioles
– Germinal centers after antigen stimulation
– Penicilli (terminal branches of arterioles)
SPLEEN
• Red pulp
– Filtration device
– Complex system of interconnected spaces
– Phagocytic macrophages
– 75% of spleen
SPLEEN
• Red pulp
– Venous sinuses (50µm in diameter) draining into the
tributaries of the splenic veins
– Reticulum (fibrocellular network)
– Splenic cords (of Billroth)
SPLEEN
• Marginal zone
– Loosly arranged lymphocytes
– Small aggregation of macrophages (periartetiolar
macrophage sheath)
• Fibrous framework
– Capsule (1.5mm thick)
– trabeculae
Thymus
• Primary lymphoid organ
• Thymus-processed lymphocytes (T
lymphocytes)
• Immune tolerance to the body’s own
components
• Neuroendocrine axis of the body
Thymus
• Largest up to age of 15 years
• Active into old age
• Pyramidal shape, red and firm in children
• Thin, gray, yellow in adult
• Two lobes
• 20g (at birth 10-15g)
Thymus
• Superior and anterior inferior mediastinum
• Level of 4th costal cartilage (lower border)
• Extends to neck
• Anterior: sternum, 4 upper ribs, sternohyoid,
sternothyroid
• Posterior: pericardium, aortic arch, left
brachiocephalic vein, trachea
Thymus
• Vessels
– Arteries: from internal thoracic and inferior thyroid
arteries
– Veins: drain to the left brachiocephalic, internal
thoracic and inferior thyroid veins
Thymus
• Innervation
– Sympathetic from stellate (cervicothoracic)
ganglion
– Parasymphathetic from vagus nerve
– Autonomic nerves are vasomotor
– Capsule of thymus recieves fibers from the phrenic
nerve
Thymus
• Outer cortex
– Densely packed cells (T lymphocytes)
– Outer cortical region(subcapsular)
• Inner medulla
– Rich in connective tissue
– Fewer lymphoid cells
Thymus
• Capsule
– Losse connective tissue
– Septa penetrate to the junction of the cortex and
medulla