Kuliah Edema
-
Upload
ranie-magezta -
Category
Documents
-
view
18 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Kuliah Edema

Edema

Definisi• Edema is a pathologic process edema bukan
penyakit
• Definisi penumpukan cairan yang berlebihan di interstitial space
• Cardiac edema edema yang berasal dari proses gagal jantung kongestif


Klasifikasi1. Berdasarkan Distribusi:
- Local : pada beberapa bagian tubuh (cth: brain edema, pulmonary edema)
- Generalized : pada seluruh tubuh (cardiac edema, renal edema)
2. Berdasarkan Penyebab:- Cardiac Edema- Renal Edema- Hepatic Edema- Idiopathic Edema

2. Berdasarkan Gravitasi:- Recessive (Non-Pitting Edema)- Frank (Pitting) Edema

Frank (Pitting – Edema)By pressing finger firmly against the tissue for a few seconds, a dent can be produced. When the finger is withdrawn, the dent may persist for several minutes.


Penyebab dan Patogenesis Penyebab Dasar:
1. Imbalance of exchange between intra-vascular and extra-vascular fluid (retention of water and sodium in the interstitial space)
2. Retention of fluid in the body (imbalance of exchange between intra- and extra-body fluid)

(1) Imbalance of exchange between intra-vascular and extra-vascular fluid
1. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP)
2. Decreased plasma colloidal OP3. Increased permeability of the capillary wall 4. Obstruction of lymphatic return5. Local factors against edema

Keseimbangan Cairan Tubuh

Sistem kapiler


Keseimbangan Hidrostatik & osmotik

• The capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP) is the capillary blood pressure.• CHP is the potential to drive the water from the vessel into interstitial space.
• The colloid osmotic pressure (COP) is formed by the proteins in the solution.
• Albumin is the main factor for the serum COP. The albumin has the highest concentration and the lowest molecular weight, so albumin has the most particles in serum.
• -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------• 1 g osmotic P. Content MW• (mmHg) (g/100 ml serum) (KD)• -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------• albumin 5.5 3.5~4.5 <70• globulin 1.4 2.5~3.8 160(IgG)• fibrinogen 1.0 0.2~0.4 >300• -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------

• The effective filtration pressure (EFP) is the difference between effective HP and effective COP.
• Lymphatic return is another way for interstitial fluid to return back to venous circulation. The lymphatic return counteracts the net effect of EFP


Lymphatic SystemThe lymphatic system provides a route
for the transport of fluids and protein away from the interstitium
System of fine lymphatic channels throughout the body passing via lymph nodes to thoracic duct
Valves ensure one-way flow

1) Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP)
1. Venous obstruction: Venous obstruction can be caused by venous congestion (thrombophlebitis, etc).
2. Arteriolar dilation : can be seen in acute inflammation and allergic responses. More blood volume will increase CHP.
3. Increased vascular volume : can occur in heart failure and pregnancy, over-infusion.
4. Effect of gravity such as prolonged standing.

Raised Capillary Pressure Cardiac failure
right ventricular failure - systemic oedema left ventricular failure - pulmonary oedema congestive cardiac failure - both
Local venous obstruction deep vein thrombosis external compression SVC obstruction

2) Decreased plasma colloidal OP1. Increased loss of plasma albumin, such as in
extensive burn, nephrotic syndrome (10g protein/day), etc.
2. Increased protein consumption in malignant tumors, chronic inflammation.
3. Decreased synthesis of plasma albumin, such as in hepatic dysfunction and starvation.
4. Dilution of serum protein due to over-infusion of water and sodium.

Reduced Oncotic PressureRenal disease
loss of albumin across glomerulusHepatic disease
inadequate albumin synthesisMalnutrition
inadequate albumin synthesis

3) Increased permeability of the capillary wall
1. In infection, the hyaluronidase released by bacteria can damage (hydrolyze the connective tissue) the capillary wall.
2. Hypoxia, acidosis, radiation damage, trauma and burn may lead to the degeneration of basement membrane of capillary.
3. Inflammatory media such as histamine(HA), kinins and 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-TH) may cause the contraction of microfilament in endothelial cells and the formation of “gap” between endothelial cells.
4. Many irritant gases (chlorine, nitrogen peroxide, ozone) and high concentration of oxygen may damage the alveolar-capillary membrane and increase the permeability of the pulmonary capillaries

(4) Obstruction of lymphatic return
1. In the patients with mammary cancer, the subaxillary lymph nodes may be removed in the radical operation.
2. The parasite enters into the lymphatic vessels in elephantiasis infestation.
The edema caused by lymph obstruction is called lymph edema.

Lymphatic ObstructionTumoursFibrosis InflammationSurgeryCongenital abnormality

5) Local factors against edema
1. The lymphatic return is increased rapidly, when the interstitial pressure begins to increase. The maximal potential of lymphatic return is to increase by 20 times.(7mmHg)
2. When the lymphatic return is increased, more protein is washed back to venous circulation with lymph, the interstitial COP will reduce. The effective COP will increase, the EFP will decrease.(4mmHg)

(2) Retention of fluid in the body
Under normal circumstances, the intake and excretion of fluid is in dynamic balance, in which the kidneys play important role. Normally the filtrate from glomeruli is 180 liter/day. 60~70% of filtrate is reabsorbed at proximal tubules, finally 99%~99.5% of filtrate is reabsorbed by renal tubules, which is called glomerular-tubular balance.

Karakteristik Edema------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Edematous causes protein appearance specific fluid concentration gravity------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------transudate ↑effective filtration 1~ 2g % clear low pressure
exudates ↑permeability of 4g % muddy high vascular wall
lymph obstruction of 4~ 5 % chyliform higher lymphatic vessel-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

Cardiac edema is caused by right heart failure. Right heart failure means:1. the output of right ventricle is
reduced2. the end-diastolic volume in right
ventricle in increased. Total venous pressure is increased.
When the patient is ambulant, the legs are firstly involved, the swelling of ankles is often the first sign.
Edema Kardiak

Liver engorgement Distention of jugular vein

Gejala gagal jantung kanan

Gejala gagal jantung

Mechanism of cardiac edema(a)Decreased cardiac output
↓myocardial contraction ↓ volume of blood pumped to the aorta ↓ renal blood supply ↑renin -angiotensin II -aldosterone system ↑reabsorption of sodium ↑ADH release the extracellular volume expanse↑water reabsorption

(b) Increased venous pressure
↓myocardial contraction of right ventricle
↑hydrostatic pressure of venule
↑effective filtration pressure stagnant hypoxia ↑vascular permeability
↑ formation of edematous fluid


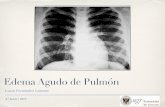
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in pulmonary interstitial space (interstitial pulmonary edema) and alveoli (alveolar pulmonary edema).
Edema Pulmonum

Pulmonary edema caused by left heart failure
Mechanism:
• The output of left ventricle is reduced, the end-diastolic volume in left ventricle in increased. Pressure of left atrium is increased. The pulmonary venous pressure is increased.
• CHP is increased.• Effective HP is increased.• Effective FP is increased.• The formation of interstitial • fluid is increased.



Congestive Heart Failure
Overall, there are TWO main effects...
1. Increased Central Venous Pressure
2. Decreased Renal Perfusion

Increased Hydrostatic Pressure:Congestive Heart Failure
Mechanism:
• The Pump is FAILING!!! Cardiac output
• Blood backs up, first into the lungs
then into the venous circulation
increasing Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
increased capillary pressure (Hydrostatic Pressure)
• Leading to Edema

Congestive Heart Failure:
& Decreased Renal Perfusion
• Congestive heart failure Decreased Cardiac Output
Decreased ARTERIAL blood volume “Less arterial blood…Less renal perfusion...
The Kidney doesn’t see enough blood coming through …….

Congestive Heart Failure:& Decreased Renal Perfusion
Decreased Renal Perfusion activates
the Renal Defense Mechanisms:1. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone axis
Na & H2O retention
2. Renal Vasoconstriction
3. Increased Renal Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH)

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS• Heart failure• Renal diseases• Cirrhosis• Nutritional origin• Idiopathic • Others

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISHEART FAILURE
• Edema initially occurs at lower part of the body (lower extremities)• symmetric location• The presence of heart diseases
cardiac enlargement gallop rhythm dyspnea
basilar rales venous distention hepatomegaly
• Noninvasive tests may be helpful echocardiography radionuclide
angiography

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISCARDIAC/RENAL DISEASE
Renal CardiacLocation onset from the face, onset from the lower periobital areas part of the bodyProgression progress quickly progress slowlyIdentity soft and mobile relatively solid, less mobileOther signs proteinuria signs of heart failure: hypertension cardiac enlargement impaired renal venous distention functional test hepatomegaly

Edema pada tungkai bawah (1)
Penyebab KeteranganGagal jantung kongestif
Simetris, timbul sebelum asites
Perikarditis konstriktiva
Simetris, tetapi timbul setelah asites; TVJ meningkat
Sirosis Pertama asites, kemudian kaki bengkak; TVJ bisa normal atau meningkat
Obstruksi vena Biasanya unilateral, satu kaki lebih berat daripada sebelahnya; jari kaki tidak terlibat
Obstruksi limfe Satu sisi lebih berat dari sisi sebelahnya; jari kaki terlibat

Edema pada tungkai bawah (2)
Stasis Obesitas Kelainan neurologis; hilangnya pompa otot kaki
Dependen dan edema stasisEdema terutama pada tungkai yang paralisis
Sindroma Nefrotik Edema umumnya melibatkan wajah; TVJ normal pada penyebab bukan jantung
Kehamilan Tungkai kiri lebih berat daripada tungkai kanan
Faktor psikogenik Wanita muda pada kondisi stres; toleransi air yang abnormal
Edema karena panas Disebabkan oleh aldosterone-mediated Na+ dan retensi air
Obat-obatan Calcium antagonist, estrogen, NSAID, steroid

APPROACH TO THE PATIENT
Generalized
Localized
or
HeartLiver
Kidney
Venous obstructionLymphatic obstruction

Tata Laksana Atasi penyebab yang mendasari Untuk mengobati simptom dapat diberikan:
furosemid 40 – 80 mg selama beberapa hari kemudian 40 mg setiap hari sebagai dosis
rumatan Penyebab gagal jantung kronik furosemid,
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker, aldosterone antagonist, beta blocker
Atasi penyebab gagal jantung kronik

Aimed at diminishing the compensatory mechanisms of low cardiac output and also improving contractility
Vasodilators—ACE inhibitors Diuretic agents Inotropic agents

Dilate blood vessels Often constricted due to activation of the
sympathetic nervous system and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Aka—ACE inhibitors
Common ACE inhibitors Captopril Lisinopril Vasotec Monopril Accupril
Nitrates

Lasix Hydrochlorothiazide(HCTZ) Spironolactone
These inhibit reabsorption of Na+ into the kidneys

Digoxin Lanoxin
Increases the contractility of the heart increasing the cardiac output

terima kasih