K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
-
Upload
wilan-dita-nesyia -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 1/36
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Dr. FITRIANI LUMONGGA
Dr. LITA FERIYAWATI
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 2/36
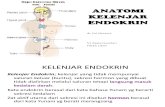
Endocrine System Parts
• Pituitary Gland
• Thyroid
• Parathyroids
• Adrenal Glands
• Pineal Body
• Reproductive Glands
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 3/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 4/36
PITUITARY
GLAND
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 5/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 6/36
There are two distinct regions in the gland:
- the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and
- the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis).
The activity of the adenohypophysis is controlled
by releasing hormones from the hypothalamus.
The neurohypophysis is controlled by nerve
stimulation
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 7/36
THE ANTERIOR LOBE OF HYPOPHYSE
is the larger and is somewhat kidney-shaped,the concavity being directed backward and
embracing the posterior lobe.
It consists of a pars anterior and a pars
intermedia, separated from each other by a
narrow cleft, the remnant of the pouch or
diverticulum.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 8/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 9/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 10/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 11/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 12/36
The pineal organ is small, weighing little more
than 0.1 gram and only about 5 to 8 millimeters
long
It lies deep within the brain between the two
cerebral hemispheres and above the thirdventricle of the spinal column.
It has a rich supply of adrenergic nerve fibers
that greatly influence its secretions
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 13/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 14/36
THYROID GLAND
(Glandula Thyreoidea)
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 15/36
Unpaired gland very variable , frequently
asymmetrical gland and highly vascularLocation: ant neck at C5-T1, overlays 2nd – 4th tracheal rings
Avg width: 12-15 mm (each lobe)
Avg height: 50-60 mm long
Avg weight: 25-30 g in adults (slightly morein women)
enlarges during menstruation and pregnancy
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 16/36
This gland is found in the neck inferior to (below)
the thyroid cartilage (also known as the Adam'sapple in men) and at approximately the same
level as the cricoid cartilage
The thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped organ andis composed of two cone-like lobes or wings:
lobus dexter (right lobe) and lobus sinister (left
lobe), and is also connected with the isthmus
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 17/36
The organ is situated on the anterior side of the neck,
lying against and around the larynx and trachea,
reaching posteriorly the oesophagus and carotidsheath.
It starts cranially at the oblique line on the thyroid
cartilage (just below the laryngeal prominence or
Adam's apple) and extends inferiorly to the fifth or
sixth tracheal ring.
It is difficult to demarcate the gland's upper and lower
border with vertebral levels because it movesposition in relation to these during swallowing.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 18/36
The thyroid gland is covered by a fibrous sheath, the
capsula glandulae thyroidea, composed of aninternal and external layer.
The external layer is anteriorly continuous with the
lamina pretrachealis fasciae cervicalis andposteriorolaterally continuous with the carotid
sheath.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 19/36
The gland is covered :
Anteriorly with infrahyoid muscles
Laterally with the sternocleidomastoid
muscle.
Posteriorly the gland is fixed to the cricoidand tracheal cartilage and cricopharyngeus
muscle by a thickening of the fascia to form the
posterior suspensory ligament of Berry
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 20/36
The thyroid isthmus is variable in presence and size,and can encompass a cranially extending pyramid
lobe (lobus pyramidalis or processus pyramidalis),
remnant of the thyroglossal duct.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 21/36
VASCULAR
ANATOMY
ARTERIAL
VEIN
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 22/36
ARTERIAL, There are three main arteries
supplying the thyroid gland:
Superior Thyroid Artery, a branch of the
external carotid artery
Inferior Thyroid Artery, a branch of the
thyrocervical trunkThyroid Ima Artery (occasionaly),
branching directly from the
brachiocephalic trunk
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 23/36
VEIN, There are three main veins draining the
thyroid gland:
Superior Thyroid Veins, draining in the
internal jugular vein
Middle thyroid vein
Inferior Thyroid Veins, draining via theplexus thyroideus impar in the left
brachiocephalic vein.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 24/36
The recurrent laryngeal nerve runs either in front of
or behind the inferior thyroid artery and it is
essential to locate this nerve during a
thyroidectomy.
The nerve is paired and arises from the vagus. It
supplies all the muscles of the larynx (except the
cricothyroid)On the right hand side, the nerve passes behind
the vagus and loops around the subclavian artery.
On the left, the nerve passes around the arch of
the aorta. The nerves pass beneath Berry'sligament (a thickened area of fascia next to the
trachea) and enter the larynx.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 25/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 26/36
PARATHYROID
GLAND
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 27/36
• Usually two on each side (superior and inferior)• Situated on the dorsal surface of the thyroid
gland
• Form and size very variable, yellowish-brown
color and have uniform smooth and shining
surface
• Length ± 6-8mm, width ± 3-4mm, thickness ±
1,5-2mm
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 28/36
PANCREAS
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 29/36
Pancreas is a mixed gland as it performs both
endocrine and exocrine functions.
Pancreas is an elongated, yellowish gland.
It consists of lobules that secrete pancreatic juice.
Interspersed at random among the lobules are
Islets of langerhans, which produce hormones.
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 30/36
It presents for examination for a caput, a cauda
and a cauda pancreatis
The caput fills up the concavity of the pars
descendens and pars inferior duodeni and is
intimately united with their walls
Anterior and inferior surfaces are covered byperitoneum
Ductus pancreaticus wirsungi begins as a delicate
duct in the cauda , extends within the substance of
the gland to the right to the caput and graduallyenlarge as it receives numerous narrow branches
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 31/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 32/36
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 33/36
Suprarenal Glands
(Glandulae
Suprarenales)
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 34/36
• Two small flat bodies, wich lie directly medial
from and above the kidneys, one on each side
• The right is approximately triangular and sits
more upon the upper pole of the kidney
• The left approximately sickle-shaped and lies
more upon the margo medial of the kidney• Facies posterior lies loosely upon the pars
lumbalis diaphragmatis
•
Facies anterior wich is in relation on the rightside with the impressio suprarenalis hepatis and
the v.cava inferior
8/11/2019 K-23, K-24 Anatomi Endokrin
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/k-23-k-24-anatomi-endokrin 35/36
There are two parts, each of which makeshormones and has a different function.
• The outer part ( Adrenal Cortex)
• The inner part (Adrenal Medulla)