Class 5 heart neck vessels.doc
-
Upload
veronicawhitman -
Category
Documents
-
view
49 -
download
1
Transcript of Class 5 heart neck vessels.doc

Heart & Neck Heart & Neck VesselsVessels

2 continuous loops2 continuous loops
Pulmonary Pulmonary circulationcirculation
Systemic circulationSystemic circulation
When the heart When the heart contracts, it pumps contracts, it pumps blood simultaneously blood simultaneously through both loopsthrough both loops

Precordium Precordium Area in anterior chest Area in anterior chest
overlying heart & great overlying heart & great vessels (major arteries & vessels (major arteries & veins connected to heart)veins connected to heart)
Heart lies from 2Heart lies from 2ndnd to 5 to 5thth ICS from right border of ICS from right border of sternum to left sternum to left midclavicular linemidclavicular line
Base at top; apex Base at top; apex pointing down to left pointing down to left lunglung
Apical impulse can be Apical impulse can be palpable in most people; palpable in most people; 55thth ICS, 7-9 cm from ICS, 7-9 cm from midsternal linemidsternal line

Great VesselsGreat Vessels Superior & inferior Superior & inferior
vena cavavena cava return return unoxygenated blood to unoxygenated blood to right side of heartright side of heart
Pulmonary arteryPulmonary artery leaves leaves right side of heart, right side of heart, bifurcates & carries bifurcates & carries venous blood to lungsvenous blood to lungs
Pulmonary veinsPulmonary veins return return freshly oxygenated freshly oxygenated blood from lungs to left blood from lungs to left side of heartside of heart
AortaAorta carries out to carries out to bodybody

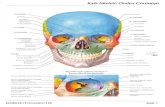
Layers of the HeartLayers of the Heart
Pericardium – tough, fibrous layer. A Pericardium – tough, fibrous layer. A sac surrounding & protecting the sac surrounding & protecting the heart, contains a few mls of serous heart, contains a few mls of serous pericardial fluid that allows for pericardial fluid that allows for smooth friction free movement of smooth friction free movement of heart muscleheart muscle
Myocardium – muscular wall of Myocardium – muscular wall of heartheart

Endocardium – thin Endocardium – thin layer of endothelial layer of endothelial tissue that lines the tissue that lines the inner surface of heart inner surface of heart chambers & valveschambers & valves
Right & left side Right & left side separated by septumseparated by septum
Atrium hold blood, Atrium hold blood, while ventricles (thick while ventricles (thick walled) are muscular walled) are muscular pumping chamberspumping chambers

Valves Valves
Unidirectional & prevent backflowUnidirectional & prevent backflow
2 AV valves (atrioventricular) 2 AV valves (atrioventricular) separate atria & ventricles. Right is separate atria & ventricles. Right is tricuspid; left is mitral (bicuspid)tricuspid; left is mitral (bicuspid)
Open during diastole, allows Open during diastole, allows ventricles to fill with bloodventricles to fill with blood
During systole, close to prevent During systole, close to prevent regurgitation back into atriaregurgitation back into atria

2 SL valves 2 SL valves (semilunar) – btw (semilunar) – btw ventricles & ventricles & arteries. Right is the arteries. Right is the pulmonic; left is pulmonic; left is aorticaortic
Open during systole Open during systole or pumping to allow or pumping to allow blood to be ejected blood to be ejected from heart (either to from heart (either to lungs or periphery)lungs or periphery)

No valves btw vena cava & right No valves btw vena cava & right atrium or pulmonary vein & left atrium or pulmonary vein & left atrium.atrium.
Therefore, abnormally high pressure Therefore, abnormally high pressure will show as…will show as…
Right side of heart – shows in neck Right side of heart – shows in neck veins & abdomenveins & abdomen
Left side of heart – shows pulmonary Left side of heart – shows pulmonary congestioncongestion

Direction of blood flowDirection of blood flow
From liver to RA via inferior vena cava; From liver to RA via inferior vena cava; superior vena cava drains venous blood superior vena cava drains venous blood from headfrom head
From RA, venous blood travels through From RA, venous blood travels through tricuspid valve to RVtricuspid valve to RV
From RV, venous blood flows through From RV, venous blood flows through pulmonic valve to pulmonary arterypulmonic valve to pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery delivers Pulmonary artery delivers unoxygenated blood to lungsunoxygenated blood to lungs

Lungs oxygenate bloodLungs oxygenate blood Pulmonary veins return oxygenated Pulmonary veins return oxygenated
blood to LAblood to LA From LA, arterial blood travels through From LA, arterial blood travels through
mitral valve to LVmitral valve to LV LV ejects blood through aortic valve into LV ejects blood through aortic valve into
aortaaorta Aorta delivers oxygenated blood Aorta delivers oxygenated blood
throughout the bodythroughout the body
Blood flows from higher pressure to Blood flows from higher pressure to lower pressurelower pressure

Cardiac cycleCardiac cycle
Diastole – ventricles are relaxed, AV Diastole – ventricles are relaxed, AV valves (tricuspid & mitral) are open. valves (tricuspid & mitral) are open. Pressure is higher in atria so blood Pressure is higher in atria so blood pours into ventricles. Toward end of pours into ventricles. Toward end of diastole, atria contract & push last diastole, atria contract & push last amount of blood out amount of blood out
Systole – so much blood in ventricles, Systole – so much blood in ventricles, ventricular pressure is higher than ventricular pressure is higher than atria & mitral & tricuspid valves close atria & mitral & tricuspid valves close to prevent regurgitation back into atriato prevent regurgitation back into atria

Closing of AV valves is 1Closing of AV valves is 1stst heart sound heart sound (S1), signals beginning of systole(S1), signals beginning of systole
The ventricular walls contract, creates The ventricular walls contract, creates pressure in ventricles (isometric pressure in ventricles (isometric contraction), the valves open & blood is contraction), the valves open & blood is ejected from right side to lungs & left ejected from right side to lungs & left side through aortaside through aorta
After contents ejected, pressure falls. After contents ejected, pressure falls. When pressure falls below that in aorta, When pressure falls below that in aorta, blood flows backward toward ventricle blood flows backward toward ventricle causing valves to closecausing valves to close
Closing of semilunar valves causes 2Closing of semilunar valves causes 2ndnd heart sound (S2) & signals end of systoleheart sound (S2) & signals end of systole

Normal Heart SoundsNormal Heart Sounds
S1 – first heart sound; closure of AV S1 – first heart sound; closure of AV valves, beginning of systole. Mitral is valves, beginning of systole. Mitral is slightly before tricuspid, but usually slightly before tricuspid, but usually heard as one. Loudest at apexheard as one. Loudest at apex
S2 – second heart sound; closure of S2 – second heart sound; closure of semilunar valves, end of systole. semilunar valves, end of systole. Aortic is slightly before pulmonic, but Aortic is slightly before pulmonic, but usually heard as one. Loudest at baseusually heard as one. Loudest at base

Split S2 – when aortic valve closes Split S2 – when aortic valve closes significantly earlier than pulmonic significantly earlier than pulmonic valve & hear them separatelyvalve & hear them separately
S3 – normally diastole is silent. S3 – normally diastole is silent. Ventricle filling causes vibration, called Ventricle filling causes vibration, called S3 or a ventricular gallop. Occurs S3 or a ventricular gallop. Occurs when ventricles are resistant to filling when ventricles are resistant to filling during early rapid filling phase (seen in during early rapid filling phase (seen in heart failure). Happens immediately heart failure). Happens immediately after S2, when AV valves are open & after S2, when AV valves are open & atrial blood first pours into ventriclesatrial blood first pours into ventricles

S4 – at the end of diastole, during S4 – at the end of diastole, during presystole. The ventricle is resistant presystole. The ventricle is resistant to filling. Atria contract & push to filling. Atria contract & push blood into a noncompliant ventricle. blood into a noncompliant ventricle. Vibrations is heard as an S4 or atrial Vibrations is heard as an S4 or atrial gallop & is heard just before S1 gallop & is heard just before S1 (occurs during coronary artery (occurs during coronary artery disease & aortic stenosis)disease & aortic stenosis)

MurmursMurmurs
Blood circulating through normal Blood circulating through normal chambers is quietchambers is quiet
If turbulent blood flow or collision – If turbulent blood flow or collision – results in a murmur, a gentle, blowing, results in a murmur, a gentle, blowing, swooshing soundswooshing sound
Seen in defects in valves – incompetent Seen in defects in valves – incompetent valve (doesn’t close completely), stenosis valve (doesn’t close completely), stenosis (valve doesn’t open completely), or (valve doesn’t open completely), or unusual openings in the chambers (wall unusual openings in the chambers (wall defects)defects)

Characteristics of Heart Characteristics of Heart MurmursMurmurs
Frequency or pitch – high pitched versus low Frequency or pitch – high pitched versus low pitched. Need a good stethoscope to hear pitched. Need a good stethoscope to hear differencedifference
Intensity or loudness – grade I (barely Intensity or loudness – grade I (barely audible), II (audible but faint), III (moderately audible), II (audible but faint), III (moderately loud, easy to hear), IV (loud, palpable thrill), V loud, easy to hear), IV (loud, palpable thrill), V (very loud), VI (loudest, can hear with steth (very loud), VI (loudest, can hear with steth off chest)off chest)
Duration – very short for heart sounds, silent Duration – very short for heart sounds, silent periods are longerperiods are longer
Timing – occurring during systole or diastoleTiming – occurring during systole or diastole Quality – blowing, roaring, rumblingQuality – blowing, roaring, rumbling Location – where it is best heardLocation – where it is best heard Radiation - transmitted downstream in the Radiation - transmitted downstream in the
direction of blood flowdirection of blood flow

Conduction Conduction SA (sinoatrial node) near superior vena SA (sinoatrial node) near superior vena
cava initiates an electrical impulse (it is cava initiates an electrical impulse (it is the pacemaker)the pacemaker)
Current flows across atria to the AV nodeCurrent flows across atria to the AV node Then the impulse travels to the bundle of Then the impulse travels to the bundle of
His, then through the ventriclesHis, then through the ventricles The electrical impulse causes the heart The electrical impulse causes the heart
muscle to contractmuscle to contract This electrical impulse spreads to the This electrical impulse spreads to the
surface & can be measured with an surface & can be measured with an ECG…ECG…

Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram ECG waves are labeled ECG waves are labeled
as PQRSTas PQRST P – depolarization of P – depolarization of
atriaatria PR interval – atrial PR interval – atrial
depolarization & depolarization & impulse travels through impulse travels through AV nodes to ventriclesAV nodes to ventricles
QRS complex – QRS complex – depolarization of depolarization of ventriclesventricles
T wave – repolarization T wave – repolarization of ventricles of ventricles

Cardiac Output Cardiac Output
Heart normally pumps 4 – 6 L of blood Heart normally pumps 4 – 6 L of blood per minute through the bodyper minute through the body
Cardiac output equals the volume of Cardiac output equals the volume of blood in each systole (or stroke blood in each systole (or stroke volume) times the number of beats volume) times the number of beats per minute (rate).per minute (rate).
CO = SV x RCO = SV x R
Preload & afterload affect heart’s Preload & afterload affect heart’s ability to increase cardiac outputability to increase cardiac output

Preload is venous return that builds Preload is venous return that builds during diastole. The length to which during diastole. The length to which ventricular muscle is stretched at ventricular muscle is stretched at the end of diastole just before the end of diastole just before contractioncontraction
The greater the stretch, the stronger The greater the stretch, the stronger the heart’s contractionthe heart’s contraction
Increased contraction results in an Increased contraction results in an increased volume of blood ejectedincreased volume of blood ejected

Afterload is the opposing pressure Afterload is the opposing pressure the ventricle must generate to open the ventricle must generate to open the aortic valve against the higher the aortic valve against the higher aortic pressureaortic pressure
After the aortic valve open, rapid After the aortic valve open, rapid ejection occursejection occurs

Neck VesselsNeck Vessels
Carotid artery – in groove Carotid artery – in groove btw trachea & sternomastoid btw trachea & sternomastoid muscle, medial to musclemuscle, medial to muscle
Jugular veins – give info Jugular veins – give info about right side of heart. about right side of heart. Reflects filling pressure & Reflects filling pressure & volumevolume
Internal jugular – larger & Internal jugular – larger & lies deep & medial to lies deep & medial to sternomastoid muscle. sternomastoid muscle. Usually not visible, although Usually not visible, although pulsation may be seen in pulsation may be seen in sternal notch when supinesternal notch when supine

External jugular – more superficial, External jugular – more superficial, lateral to sternomastoid muscle & above lateral to sternomastoid muscle & above clavicleclavicle
Arterial pulse – forward propulsion of Arterial pulse – forward propulsion of bloodblood
Jugular pulse – backwashJugular pulse – backwash
From jugular veins can assess the From jugular veins can assess the central venous pressure (CVP) or heart’s central venous pressure (CVP) or heart’s efficiency as a pumpefficiency as a pump

Orthostatic Blood Orthostatic Blood PressurePressure
Orthostatic hypotension – drop in blood Orthostatic hypotension – drop in blood pressure with position changes from lying pressure with position changes from lying to sitting to standing. Drop of 20mmHg to sitting to standing. Drop of 20mmHg systolic and/or drop of 10mmHg diastolicsystolic and/or drop of 10mmHg diastolic
S & S – dizziness, lightheaded, pallor, S & S – dizziness, lightheaded, pallor, diaphoresisdiaphoresis
Supine for 5-10min, do bp; sit on side of Supine for 5-10min, do bp; sit on side of bed for 2 min, take bp; stand for 2min, bed for 2 min, take bp; stand for 2min, take bptake bp
Arm MUST be supported at heart levelArm MUST be supported at heart level

Subjective DataSubjective Data
Chest painChest pain Dyspnea (SOB)Dyspnea (SOB) CoughCough FatigueFatigue Cyanosis or pallorCyanosis or pallor EdemaEdema Hx cardiac problemsHx cardiac problems Family Hx cardiac problemsFamily Hx cardiac problems