15 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN
-
Upload
riska-arista-yulianti -
Category
Documents
-
view
173 -
download
17
Transcript of 15 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN

CURICULUM VITAE
Name : Mulyadi M. Djer, MD, SpA(K), PhDPlace / Date of Birth : Padang, 29 October 1964Adress : Jl. Taman Sari VIII/23, Jatinegara Baru, Buaran, Jakarta Timur 13940. Phone 021 48636322Current Position : Lecturer and Medical Staff, Department of Child Health FKUI-RSCM JakartaOrganization : Secretary of Indonesia Society of Pediatric Cardiology (Perkani)
Educational Qualifications:Year: 1989 Degree: Medical Doctor (MD)
Institution: FKUI 1997 Pediatric Specialist (SpA) FKUI
2003 Pediatric Cardiologist FKUI
2005 Consultant Pediatric Cardiologist [(SpA(K)] IDAI
2008 Doctor of Phylosophy (PhD) FKUI
Awards, Fellowship, Grants:2001-2002 Fellowship training in Pediatric Cardiology at Institut Jantung
Negara (National Heart Institute), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2004 Live course in Pediatric Cardiac Intervention, Beijing, China2004 & 2006 Live course in Pediatric Catheter Intervention , Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia2004 Short course in Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care, Miami, USA2005 & 2007 International Workshop on Interventional Pediatric Cardiology, Millan, Italy2005 Live course in Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Emerging
New Technique in Cardiac Surgery, Buenos Aires, Argentina2006 Live course in Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Adult
Congenital Heart Disease, Las Vegas, USA 2009 Live course in Pediatric and Adult Interventional Cardiac
Symposium, Cairns, Australia

Heart Disease in Infant and Children
Heart Disease in Infant and Children
Mulyadi M. Djer, MD, SpA(K), PhD
Mulyadi M. Djer, MD, SpA(K), PhD
Department of Child HealthMedical School University of Indonesia
Department of Child HealthMedical School University of Indonesia

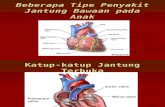
Structures of the heart

Cardiac performanceCardiac performance
PreloadAfterloadContractilityRate
PreloadAfterloadContractilityRate


Normal Heart

Heart disease in childrenHeart disease in children Congenital heart disease
Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc
Congenital heart disease Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc

Heart disease in childrenHeart disease in children Congenital heart disease
Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc
Congenital heart disease Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc

Heart disease in childrenHeart disease in children Congenital heart disease
Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc
Congenital heart disease Acyanosis congenital heart disease Cyanosis congenital heart disease
Acquired heart disease Acute rheumatic fever Chronic rheumatic heart disease Kawasaki disease Cardiac involvement in systemic disease
Thalasemia Kidney disease etc

Congenital Heart DiseaseCongenital Heart Disease

Incidence of Congenital Heart DiseaseIncidence of Congenital Heart Disease The incidence: 8-10 in 1000 live birth
Indonesia: Total population : ± 235,000,000 Birth rate: 2.3 % Incidence CHD per year: 50,000
cases
The incidence: 8-10 in 1000 live birth Indonesia:
Total population : ± 235,000,000 Birth rate: 2.3 % Incidence CHD per year: 50,000
cases

Classification of CHDClassification of CHD Acyanosis
Normal pulmonary blood flow Pulmonary Stenosis (PS) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Coarctatio Aorta (CoA)
Increased pulmonary blood flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Atrial Septal Dfect (ASD) Ventricular Sseptal Defect (VSD)
Cyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
TGA without PS Increased pulmonary blood flow
TGA with VSD Truncus arteriosus Total anomaly pulmonary vein drainage
Decreased pulmonary blood flow ToF Pulmonary atresia Ticuspid atresia
Acyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
Pulmonary Stenosis (PS) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Coarctatio Aorta (CoA)
Increased pulmonary blood flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Atrial Septal Dfect (ASD) Ventricular Sseptal Defect (VSD)
Cyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
TGA without PS Increased pulmonary blood flow
TGA with VSD Truncus arteriosus Total anomaly pulmonary vein drainage
Decreased pulmonary blood flow ToF Pulmonary atresia Ticuspid atresia

Classification of CHDClassification of CHD Acyanosis
Normal pulmonary blood flow PS AS CoA
Increased pulmonary blood flow PDA ASD VSD
Cyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
Transposition of Great Artery (TGA) without PS Increased pulmonary blood flow
TGA with VSD Truncus arteriosus Total anomaly pulmonary vein drainage (TAPVD)
Decreased pulmonary blood flow Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) Pulmonary atresia (PA) Ticuspid atresia
Acyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
PS AS CoA
Increased pulmonary blood flow PDA ASD VSD
Cyanosis Normal pulmonary blood flow
Transposition of Great Artery (TGA) without PS Increased pulmonary blood flow
TGA with VSD Truncus arteriosus Total anomaly pulmonary vein drainage (TAPVD)
Decreased pulmonary blood flow Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) Pulmonary atresia (PA) Ticuspid atresia

Perbedaan Sirkulasi Janin dan Neonatus
Perbedaan Sirkulasi Janin dan Neonatus

Changes in Pulmonary Vascular Resistance 7 weeks preceding birth, at birth and 7 weeks after birth
Changes in Pulmonary Vascular Resistance 7 weeks preceding birth, at birth and 7 weeks after birth
Park MK. Pediatric cardiology for practitioner. 5th Ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2008

Pathophysiology acyanotic and cyanotic Pathophysiology acyanotic and cyanotic
Hemodynamic acyanoticHemodynamic acyanotic Hemodynamic cyanoticHemodynamic cyanotic

Critically Congenital Heart DiseaseCritically Congenital Heart Disease Complex CHD in which circulation to
lungs /systemic depend on PDA Duct dependency pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary Atresia Duct deppendent systemic circulation
Hypoplastic left heart syndrom Duct deppendent systemic circulation
Transposition of great artery
Complex CHD in which circulation to lungs /systemic depend on PDA Duct dependency pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary Atresia Duct deppendent systemic circulation
Hypoplastic left heart syndrom Duct deppendent systemic circulation
Transposition of great artery

Critically CHDCritically CHD
Duct Dependent PulmonaryCirculation
Duct Dependent Systemic Circulation
Duct Dependent Mixing Circulation

PDA
Located between aorta and pulmonary arteryLocated between aorta and pulmonary artery

ASD
Defect between LA and RADefect between LA and RA

VSD VSD

Tetralogy Fallot
Syndrome consist of 4 items: VSD Pulmonary stenosis Aortic over-riding RVH
Syndrome consist of 4 items: VSD Pulmonary stenosis Aortic over-riding RVH

Transposition of Great arteryTransposition of Great artery

EtiologyEtiology
Genetic 10 % Chromosome 7 % Monogenic 3 %
Environment 3 % Multifactor 90 %
Genetic 10 % Chromosome 7 % Monogenic 3 %
Environment 3 % Multifactor 90 %

Sign and Symptom of CHDSign and Symptom of CHD Cyanosis Dyspneu Exercise intolerance
Infant Feeding problem Intermittent feeding Prolonged feeding
Big children Dyspneu on exertion Orthopneu Recurrent respiratory tract infection Poor weight gain Asymptomatic murmur
Cyanosis Dyspneu Exercise intolerance
Infant Feeding problem Intermittent feeding Prolonged feeding
Big children Dyspneu on exertion Orthopneu Recurrent respiratory tract infection Poor weight gain Asymptomatic murmur

Cyanosis Central VS. PheripheralCyanosis Central VS. Pheripheral
Lefkowitz B, 2000
Central Mucous
membrane Mouth, tongue
Pheripheral Acral
Central Mucous
membrane Mouth, tongue
Pheripheral Acral


No murmur does not exclude CHD
The presence of murmur does not mean that there is CHD
No murmur does not exclude CHD
The presence of murmur does not mean that there is CHD

DiagnosisDiagnosis Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI
Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI

DiagnosisDiagnosis Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI
Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI

How to read chest X rayHow to read chest X ray

ElectrocardiographyElectrocardiography
Cardiac Potential Cardiac Potential action recording on action recording on ECC electrode placing ECC electrode placing on the surface of the on the surface of the bodybody
Reference value Reference value ageage
Cardiac Potential Cardiac Potential action recording on action recording on ECC electrode placing ECC electrode placing on the surface of the on the surface of the bodybody
Reference value Reference value ageage

DiagnosisDiagnosis Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI
Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI

EchocardiographyEchocardiography

DiagnosisDiagnosis Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI
Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI

Atrial septal defectAtrial septal defect
ASD ASD

DiagnosisDiagnosis Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI
Clinical finding Supporting examination
Level 1 Periphery blood examination Arterial blood gas analysis Chest X ray Electrocardiography
Level 2 Echocardiography
Level 3 Cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic Therapeutic
Others CT Scan MRI



MR-guided diagnostic and interventional proceduresMR-guided diagnostic and interventional procedures

Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.
Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.

Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment Severe CoA / Interrupted Ao arch: as soon
as possible TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.
Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment Severe CoA / Interrupted Ao arch: as soon
as possible TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.

Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.
Early diagnosis is important because: Management of disease and education to
parent depend on it Certain CHD has optimal age to undergo
definitive treatment TGA: 2 weeks Complete AVSD: 3-6 months Truncus arteriosus: < 6 months
Most CHD does not need intervention / surgery at time of diagnosis:
Intervention / surgery will be needed at any age in which the risk of intervention or surgery is low (usually above 1-2 year), but don’t late.
Early surgery / intervention is needed if conservative treatment fail.

Management of CHD Management of CHD
Transcatheter Intervention
HybridIntervention
Surgery
Palliative Definitive
Medical Treatment

Management of Congenital Heart DiseaseManagement of Congenital Heart Disease
Do not required treatment or intervention, some of defect closed spontaneously
Treatment Medical treatment
Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD
Do not required treatment or intervention, some of defect closed spontaneously
Treatment Medical treatment
Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD

Treatment of Congenital Heart DiseaseTreatment of Congenital Heart Disease
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD

Treatment of Congenital Heart DiseaseTreatment of Congenital Heart Disease
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD

Treatment of Congenital Heart DiseaseTreatment of Congenital Heart Disease
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD
Medical treatment Initial treatment (PGE1, indomethacin) Complication treatment (anti failure, anti spell) Conservative treatment (Eisenmenger)
Palliative Intervention non-surgery (BAS, PDA stenting) Surgery (BT shunt, PA banding)
Definitive Intervention non-surgery Non-complex CHD Surgery Complex CHD

Medical TreatmentMedical Treatment1. Initial treatment: Prostaglandin E1
Critical CHD To open PDA Fast response Doses 10 nanogram/kg/minute Side effect:
Apneu Hypotension
1. Initial treatment: Prostaglandin E1
Critical CHD To open PDA Fast response Doses 10 nanogram/kg/minute Side effect:
Apneu Hypotension

...Medical treatment...Medical treatment
2. Complication treatmentCyanotic spella. Kneechest positionb. Acid-base correctionc. Sedation: Morphin sulphat 0,2 mg/kg
IM/SCd. Propranolol: 0,01-0,25 mg/kg
(average 0,05 mg/kg) IV slowly
2. Complication treatmentCyanotic spella. Kneechest positionb. Acid-base correctionc. Sedation: Morphin sulphat 0,2 mg/kg
IM/SCd. Propranolol: 0,01-0,25 mg/kg
(average 0,05 mg/kg) IV slowly

...Medical treatment...Medical treatmentHeart failure ↓ preload
Diuretic; Frusemide : 1-2mg/kg/day 2 X
Sprironolakton:
0-10 kg: 6,25mg/kg 2X; 11-20 kg: 12,5 mg/kg 2X; 21-40 kg: 25 mg/kg 2X; >40 kg: 25 mg/kg 3X
↓ afterload Vasodilator
Captopril: 0,3-6 mg/kg/day divided 2-3 dose
Heart failure ↓ preload
Diuretic; Frusemide : 1-2mg/kg/day 2 X
Sprironolakton:
0-10 kg: 6,25mg/kg 2X; 11-20 kg: 12,5 mg/kg 2X; 21-40 kg: 25 mg/kg 2X; >40 kg: 25 mg/kg 3X
↓ afterload Vasodilator
Captopril: 0,3-6 mg/kg/day divided 2-3 dose

...Medical treatment...Medical treatment ↑ Contractility
Dopamine : 5-10µg/kg/minute Dobutamine: 5-10 µg/kg/minute Digoxin (µg/kg/day)
Digitalization Maintenance
Premature 20 5 < 30 day 30 8 < 2 year 40-50 10-12 > 2 year 30-50 8-10
↑ Contractility Dopamine : 5-10µg/kg/minute Dobutamine: 5-10 µg/kg/minute Digoxin (µg/kg/day)
Digitalization Maintenance
Premature 20 5 < 30 day 30 8 < 2 year 40-50 10-12 > 2 year 30-50 8-10

↓ heart rate Adenosine: 0,1 mg/kg fastly Beta blocker: Propranolol: 0,01-0,25 mg/kg (average 0,05 mg/kg) IV slowly.
↓ heart rate Adenosine: 0,1 mg/kg fastly Beta blocker: Propranolol: 0,01-0,25 mg/kg (average 0,05 mg/kg) IV slowly.

PalliativePalliative
Aim: to release sign or symptom Non-surgery:
BAS PDA stenting
Surgery: BT Shunt PA banding
Aim: to release sign or symptom Non-surgery:
BAS PDA stenting
Surgery: BT Shunt PA banding

Definitive TreatmentDefinitive Treatment
Non-surgery: Non-Complex CHD Surgery:
Bi-ventricular circulation Single-ventricular /univentricular
circulation One and half ventricle Heart transplantation
Non-surgery: Non-Complex CHD Surgery:
Bi-ventricular circulation Single-ventricular /univentricular
circulation One and half ventricle Heart transplantation

ComplicationsComplications Heart failure
preload afterload contractility heart rate
Cyanotic spell Endocarditis Eisenmenger syndrome etc
Heart failure preload afterload contractility heart rate
Cyanotic spell Endocarditis Eisenmenger syndrome etc

Ventricular Septal DefectVentricular Septal Defect

VSD VSD

RA
RV
RA LALA
RV LVLV
Ventricular septal defect


Ventricular septal defectVentricular septal defect Management:
Medical treatment Anti-failure
Digoxin Diuretic
Palliative PA banding
Definitive : VSD closure
Surgery Transcatheter closure
Management: Medical treatment
Anti-failure Digoxin Diuretic
Palliative PA banding
Definitive : VSD closure
Surgery Transcatheter closure

VSDVSD
Heart failure (+)Heart failure (+) Heart failure (-)Heart failure (-)
Anti failureAnti failure
FailFail SuccessSuccess
PABPAB
Evaluate in 6 mothsEvaluate in 6 moths
Surgical closure/Transcatheter closureSurgical closure/Transcatheter closure
Aortic valve prolaps
Aortic valve prolaps
Infundibular stenosis
Infundibular stenosis
PHPH SmallerSmallerSpontaneousclosure
Spontaneousclosure
CathCath
PVD(-)PVD(-) PVD(+)PVD(+) CathCath
CathCath
ReactiveReactive Non-reactive
Non-reactive
ConservativeConservative
FR>1.5FR>1.5FR<1.5FR<1.5


….VSD Occlusion Amplatzer Perimembranous VSD Occluder
….VSD Occlusion Amplatzer Perimembranous VSD Occluder

Amplatzer Perimembranous VSD OccluderAmplatzer Perimembranous VSD Occluder

Ventricular septal defectVentricular septal defect
VSD before occlusionVSD before occlusion

Ventricular septal defectVentricular septal defect
Snaring wire at PA and pull it out to FV
Snaring wire at PA and pull it out to FV

Ventricular septal defectVentricular septal defect
VSD during deploying the deviceVSD during deploying the device

VSD after occludedusing ASOVSD after occludedusing ASO

…VSD Surgery…VSD Surgery

Interventional Treatment of Congenital Heart disease
Interventional Treatment of Congenital Heart disease

Invasiveness
Effe
ctiv
enes
s
Good
Bad
State of ArtState of Art
Intervention
Minimal InvasiveSurgery
ConventionalSurgery

Transcatheter treatment of CHD offers a number of advantages over surgery
Transcatheter treatment of CHD offers a number of advantages over surgery
Less invasive Fast recovery Eliminates thoracotomy No surgical complication No post surgical pain No chest scar Shortened hospitalization Minimal hospital service
requirements
Less invasive Fast recovery Eliminates thoracotomy No surgical complication No post surgical pain No chest scar Shortened hospitalization Minimal hospital service
requirements

SurgerySurgery InterventionIntervention

Interventional treatment in CHDInterventional treatment in CHDPalliative
Balloon atrial septectomy (BAS)PDA stenting
DefinitivePercutaneous occlusion of cardiac defect
PDA, ASD,VSDCollateralArtery-venous malformation
Balloon angioplasty / valvuloplasty Balloon valvuloplasty: PS, AS or MSBalloon dilatation / stent branch of pulmonary artery stenosisBalloon angioplasty Coarctation of aortaRadio frequency assisted valvotomi in PA-IVS
PalliativeBalloon atrial septectomy (BAS)PDA stenting
DefinitivePercutaneous occlusion of cardiac defect
PDA, ASD,VSDCollateralArtery-venous malformation
Balloon angioplasty / valvuloplasty Balloon valvuloplasty: PS, AS or MSBalloon dilatation / stent branch of pulmonary artery stenosisBalloon angioplasty Coarctation of aortaRadio frequency assisted valvotomi in PA-IVS

020406080
100120140160180
PDA ADO ASD VSD
RSCM RSJHK RS SOETOMO RS M HOESIN RS SARDJITO
020406080
100120140160180
PDA ADO ASD VSD
RSCM RSJHK RS SOETOMO RS M HOESIN RS SARDJITO
175
66
145 1
75
94
7 0 0
204 0 0 0
Interventional Pediatric Cardiology in IndonesiaInterventional Pediatric Cardiology in Indonesia